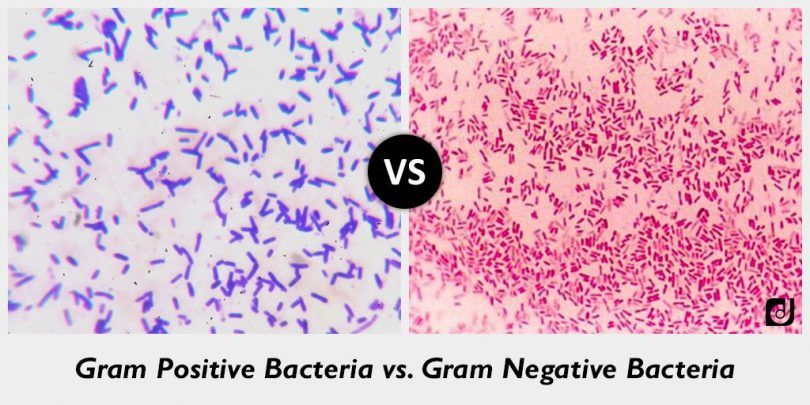
The Gram-Stain is the single most common and cost-effective staining technique used in identifying bacterial organisms. The method was originally devised in 1884 by a Danish bacteriologist, Hans Christian Gram.
This is the method used to differentiate two types of bacteria based on the structural differences in their cell walls. In this test, bacteria that retain the crystal violet dye do so because of a thick layer of peptidoglycan and are called Gram-positive bacteria.
To better understand the slippery distinctions between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria; let’s take a brief look at the definitions with their examples.
Gram Positive Bacteria
In most of the gram-positive bacteria, the cell wall consists of many layers of peptidoglycan which forms a thick and rigid structure. The cell wall of the gram-positive also contains teichoic acids which are made up of alcohol and phosphate.
The cell wall is called murein. The peptidoglycan is made from repeating units of NAG (N-acetylglucosamine) and NAM (N-acetylmuramic acid). The repeating units of NAM and NAG make thick interlinked parallel layers to form a cell wall.
The linking between the parallel layers of peptidoglycan is due to the formation of a peptide linkage between the short peptide (4 amino acids; commonly L-alanine, and D-glutamate, meso-diaminopimelic acid and D-alanine) by the action of transpeptidase.
- Example:- Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, etc.
Gram Negative Bacteria
The cell wall is made up of a few layers of peptidoglycan and an outer membrane. The outer membrane is made up of LPS (Lipopolysaccharides), lipoproteins, and phospholipids.
The peptidoglycan remains bound to lipoproteins of the outer membrane. It is present in the periplasm which is a gel-like fluid between the outer membrane and the plasma membrane. The cell wall of gram-negative bacteria lacks the teichoic acid.
There are three major components of LPS: Lipid A, Core polysaccharide, and the O-polysaccharide. Lipid A is the lipid portion of the LPS which is embedded in the top layer of the outer membrane. The core polysaccharide is attached to lipid A and consists of unusual sugars, providing stability.
- Example:- Escherichia, Salmonella, etc.
Learn about the difference between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
Gram Reaction
Gram positive bacteria retain Crystal violet dye and stain dark violet or purple, with gram stain when washed with absolute alcohol and water whereas Gram negative bacteria can be decolonized to accept counter stain, red or pink, they don’t retain the Gram stain.
Peptidoglycan Layer
Gram positive bacteria is thick or multi-layered while Gram negative bacteria is thin or single layered.
Antibiotic Resistance
Gram positive bacteria are more susceptible to antibiotics whereas Gram negative Bacteria are more resistant to antibiotics.
Flagella Structure
A gram positive bacterium is composed of 2 rings in the basal body while Gram negative Bacteria have 4 rings in basal body.